Org Workflows Executor – Introduction
Org Workflows Executor is a service framework designed to register, manage, and execute domain-specific logic workflows associated with organizational automation. These workflows are defined using a structured DSL (Domain-Specific Language) and can be executed locally or remotely based on configuration.
This system provides:
- A structured format to register and store workflows in a backend data store.
- A WebSocket-based interface for submitting workflow execution requests and receiving outputs asynchronously.
- A RESTful API for creating, updating, deleting, and querying workflow definitions.
- A queue-based task executor that decouples execution from client interaction, supporting scalable asynchronous processing.
- Support for remote and local DSL execution, enabling integration across distributed environments.
Architecture
The Org Workflows Executor architecture is designed to handle the registration, validation, search, execution, and result handling of organizational DSL workflows in a scalable and modular fashion. The system separates concerns between input validation, workflow resolution, execution, and subject-level intervention—ensuring traceable and secure handling of automation requests.
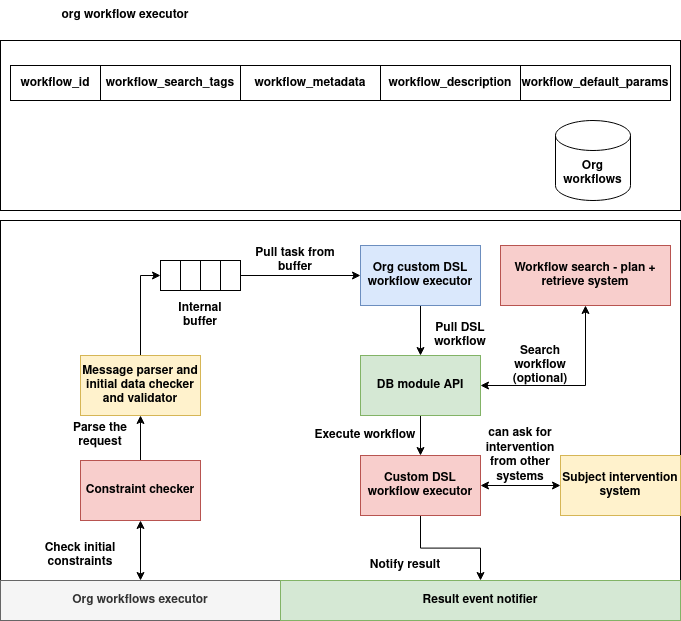
The architecture is composed of the following coordinated subsystems:
1. Org Workflows Registry
At the top of the architecture is the Org Workflows Data Store, which contains all registered DSL workflows. Each workflow is uniquely identified and indexed by metadata and tags to support fast search and classification.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
workflow_id |
Unique identifier for the workflow |
workflow_search_tags |
Tags to categorize workflows (e.g., "analytics", "alerts") |
workflow_metadata |
DSL structure, module map, versioning, etc. |
workflow_description |
Human-readable explanation of the workflow |
workflow_default_params |
Global parameters provided at execution time |
Workflows are queried either directly (by ID) or discovered through metadata using the Workflow Search – Plan + Retrieve System.
2. Input Parsing and Validation Pipeline
Incoming DSL execution requests—via WebSocket or internal APIs—are processed by a structured validation pipeline before dispatch:
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Constraint Checker | Validates high-level structural or policy constraints on the request |
| Message Parser and Initial Data Checker | Ensures required parameters, fields, and workflow identifiers are present and well-formed |
| Internal Buffer | Temporarily queues validated execution requests for asynchronous processing |
This pipeline is critical in safeguarding the system from malformed, unauthorized, or ambiguous requests.
3. DSL Execution Orchestration
Validated requests are dequeued from the buffer and passed to the Org Custom DSL Workflow Executor. This executor is responsible for:
- Pulling the workflow definition from the database (via DB Module API)
- Managing optional search-based retrieval if only partial metadata is supplied
- Executing the DSL logic using the internal Custom DSL Workflow Executor
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Org Custom DSL Workflow Executor | High-level dispatcher that binds DSL definitions to executions |
| DB Module API | Interfaces with the Org Workflows Database for read operations |
| Custom DSL Workflow Executor | Executes the task using the DSL engine and configured execution graph |
4. Subject Intervention Support
The Custom DSL Workflow Executor can optionally request subject-level interventions from external human or system actors using the Subject Intervention System.
This allows workflows to pause, wait for external approval or input, and resume execution conditionally—enabling complex, interactive automation scenarios.
5. Output Notification
Upon completion of DSL execution, the output (or failure reason) is relayed via the Result Event Notifier back to the origin of the request (typically over WebSocket). This module ensures correct correlation of results using UUIDs and closes the session cleanly.
Execution Flow Summary
- Receive Task: Task is received via WebSocket and pushed into an internal buffer.
- Validate Request: Constraint checker and data validator verify correctness.
- Resolve Workflow: Workflow is fetched either directly or via metadata query.
- Execute DSL: DSL is executed with inputs; external intervention may be requested.
- Notify Result: Result is emitted back to the client over WebSocket.
Subsystem Mapping
| Subsystem | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| WebSocket Server | Entry point for DSL execution requests |
| Buffer & Validator Pipeline | Frontline parsing and structural validation |
| Workflow Search & DB API | Workflow lookup by ID or metadata |
| DSL Executor | Execution of the registered DSL logic |
| Subject Intervention System | External human/system decision integration |
| Result Event Notifier | Response streaming to clients post-execution |
Key Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
OrgDSLWorkflows |
A data class representing the DSL workflow definition and associated metadata |
OrgDSLWorkflowsDatabase |
A backend data access layer for managing workflow definitions |
DSLExecutor |
Executes a given DSL workflow with user-provided input and configuration |
DSLTaskExecutor |
Background processor that consumes tasks from a queue and runs executions |
| WebSocket Server | Receives execution tasks, tracks results by session, and streams outputs |
| Flask API Server | Provides REST endpoints for workflow lifecycle management |
This design allows flexible integration with internal systems or external services needing runtime DSL execution, while maintaining operational decoupling and clear separation of responsibility.
Workflow Schema
OrgDSLWorkflows Data Class
from dataclasses import dataclass, field, asdict
from typing import List, Dict, Any
@dataclass
class OrgDSLWorkflows:
workflow_id: str = ''
workflow_search_tags: List[str] = field(default_factory=list)
workflow_metadata: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=dict)
workflow_description: str = ''
workflow_default_params: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=dict)
@classmethod
def from_dict(cls, data: Dict[str, Any]) -> "OrgDSLWorkflows":
return cls(
workflow_id=data.get("workflow_id", ""),
workflow_search_tags=data.get("workflow_search_tags", []),
workflow_metadata=data.get("workflow_metadata", {}),
workflow_description=data.get("workflow_description", ""),
workflow_default_params=data.get("workflow_default_params", {})
)
def to_dict(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {
"workflow_id": self.workflow_id,
"workflow_search_tags": self.workflow_search_tags,
"workflow_metadata": self.workflow_metadata,
"workflow_description": self.workflow_description,
"workflow_default_params": self.workflow_default_params
}
| Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
workflow_id |
str |
Unique identifier for the workflow. Acts as the primary key in storage. |
workflow_search_tags |
List[str] |
List of tags for classifying and searching workflows by keywords. |
workflow_metadata |
Dict[str, Any] |
Contains structural information such as version, modules, or execution graph. |
workflow_description |
str |
Human-readable description of what the workflow does. |
workflow_default_params |
Dict[str, Any] |
Default settings and global parameters used when executing the workflow. |
REST APIs
API: Create DSL Workflow
Endpoint: POST /dsl
Description: Registers a new DSL workflow from a JSON definition.
Request Body (JSON)
{
"workflow_id": "sample_workflow",
"workflow_search_tags": ["analytics", "daily"],
"workflow_metadata": {
"name": "Sample Workflow",
"version": {"version": "1.0", "releaseTag": "stable"},
"graph": {},
"modules": {}
},
"workflow_description": "Performs daily data analysis",
"workflow_default_params": {
"globalSettings": {"timezone": "UTC"},
"globalParameters": {"threshold": 0.8}
}
}
cURL Example
curl -X POST http://localhost:8000/dsl \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d @workflow.json
API: Get DSL Workflow by ID
Endpoint: GET /dsl/<workflow_id>
Description: Retrieves a DSL workflow definition by ID.
cURL Example
curl http://localhost:8000/dsl/sample_workflow
API: Update DSL Workflow
Endpoint: PUT /dsl/<workflow_id>
Description: Updates a workflow by setting new field values.
Request Body (JSON)
{
"workflow_description": "Updated description",
"workflow_search_tags": ["realtime", "monitoring"]
}
cURL Example
curl -X PUT http://localhost:8000/dsl/sample_workflow \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"workflow_description": "Updated description"}'
API: Delete DSL Workflow
Endpoint: DELETE /dsl/<workflow_id>
Description: Deletes a DSL workflow from the store.
cURL Example
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:8000/dsl/sample_workflow
API: Query DSL Workflows
Endpoint: POST /dsls
Description: Query workflows by filters such as tags, metadata, or ID.
Request Body (JSON)
{
"workflow_search_tags": { "$in": ["analytics"] }
}
cURL Example
curl -X POST http://localhost:8000/dsls \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"workflow_search_tags": {"$in": ["analytics"]}}'
API: Register DSL Entry from External DSL Registry
Endpoint: POST /dsl/register/<dsl_id>
Description: Pulls DSL definition from external source (via DSLDBClient) and registers it.
cURL Example
curl -X POST http://localhost:8000/dsl/register/sample_workflow
Notes
- All responses follow a standard JSON format:
Success response:
json
{
"success": true,
"data": { ... }
}
Error response:
json
{
"success": false,
"error": "Reason for failure"
}
WebSocket Server
The WebSocket server in Org Workflows Executor enables real-time DSL execution. Clients connect to the server, submit execution requests, and receive outputs over the same connection. The server maintains a mapping of active tasks using UUIDs and ensures that responses are sent back to the correct requester.
WebSocket Endpoint
URL: ws://<host>:8765
Protocol: WebSocket
Request Format (JSON)
{
"workflow_id": "sample_workflow",
"input_data": {
"user_input": { "x": 10 }
},
"output_name": "result"
}
Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
workflow_id |
string |
The registered workflow ID to be executed |
input_data |
object |
The input payload to pass to the DSL executor |
output_name |
string |
The key to extract from the output result |
Response Format (on Acceptance)
{
"success": true,
"uuid": "a245f83a-efc4-4ecf-a3b0-07186a04a9fd"
}
Response Format (on Completion)
{
"success": true,
"output": {
"result": 12
}
}
Response Format (on Error)
{
"success": false,
"error": "Workflow not registered"
}
Behavior Summary
-
When a client sends a task, the server:
-
Validates
workflow_idagainst the internal store. - Generates a unique UUID and registers the WebSocket connection.
- Queues the task for execution via
DSLTaskExecutor. - When execution completes, sends the result to the client using the same socket.
- Closes the connection after sending the response.
Python WebSocket Client Example
import asyncio
import websockets
import json
async def run_dsl_workflow():
uri = "ws://localhost:8765"
async with websockets.connect(uri) as websocket:
request_payload = {
"workflow_id": "sample_workflow",
"input_data": { "user_input": { "x": 10 } },
"output_name": "result"
}
await websocket.send(json.dumps(request_payload))
while True:
response = await websocket.recv()
response_data = json.loads(response)
print("Response:", response_data)
if "output" in response_data or "error" in response_data:
break
asyncio.run(run_dsl_workflow())
Requirements
- The workflow must be registered in the system (via
/dslor/dsl/register/<dsl_id>). - The WebSocket connection remains open until a result or error is returned.
- Each connection is one-shot per task (one task per connection).