Orgs registry
1. Introduction
The OrgObject API allows clients to manage organization metadata stored in MongoDB. It supports:
- Creating, retrieving, updating, and deleting organizations
- Filtering based on organization metadata, spec versions, tags, groups, etc.
- GraphQL endpoint for flexible queries
The service is intended to support registry-based, tagged, and spec-linked metadata for multiple organizations across systems.
Architecture
The Orgs Registry System is a distributed metadata indexing and query infrastructure designed to manage, store, and search metadata for organizational entities. It provides structured APIs to register organizations, update or delete them, and query organization-specific data using REST, GraphQL, and DSL-based search interfaces.
This registry supports group-level hierarchy resolution, access controls, resource indexing, and skills tagging — enabling powerful discovery of organizational capabilities across federated registries. Backed by a pluggable database layer and middleware-driven search resolution, the registry is optimized for both static and dynamic metadata operations.
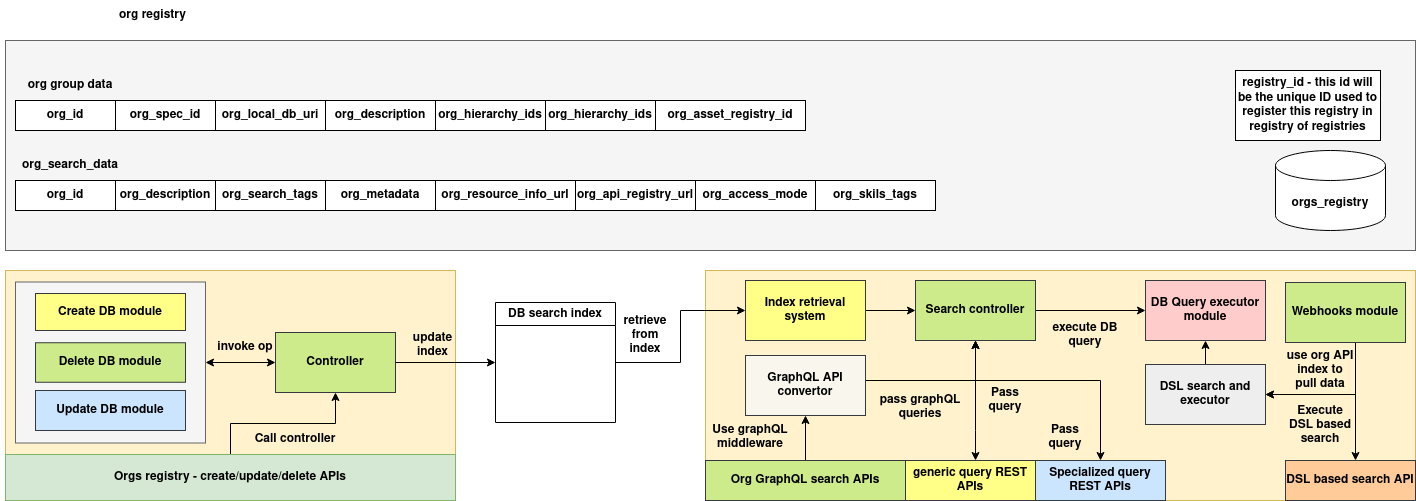
1. Organization Metadata Management
This subsystem handles the lifecycle of organization metadata entries — including creation, updates, and deletions. Each entry is identified using a globally unique registry_id and stored in the central orgs_registry database.
2. Registry Operations Controller
This subsystem acts as the execution layer for all CRUD operations related to organizational registration.
Create DB Module
Handles creation of new organization entries. Validates schema, persists group and search data, and updates the DB search index.
Update DB Module
Manages updates to existing org metadata. Ensures backward-compatible updates and index synchronization.
Delete DB Module
Deletes org entries and performs cascading deletions on related indices when required.
Controller
Central interface that receives API calls and routes them to the corresponding operation module (create/update/delete). Also triggers index updates post-operation.
3. Search Infrastructure and Query Layer
This subsystem provides various ways to search, filter, and retrieve organization metadata using REST, GraphQL, and DSL-based interfaces.
DB Search Index
A precomputed index used for efficient query resolution. Populated and updated by the controller during CRUD operations.
Index Retrieval System
Retrieves relevant indexed data based on the incoming search criteria. Used in both API and DSL search pipelines.
Search Controller
Executes search queries and routes results to the caller. Supports middleware-driven query dispatch to different resolution engines.
4. API Interfaces
This system supports three types of search APIs for querying org data:
Generic Query REST APIs
Expose endpoints to filter organizations using common query parameters (e.g., tags, metadata, access mode).
Specialized Query REST APIs
Tailored endpoints for high-specificity use cases (e.g., search by asset registry ID, API exposure mode, or skill clusters).
GraphQL Search APIs
GraphQL schema provides flexible search over org fields using a middleware layer. Enables nested and selective queries.
GraphQL API Converter
Translates GraphQL input queries into DB-compatible search expressions and invokes the search controller.
5. DSL-Based Search Engine
This subsystem allows more complex and programmable search behavior through a DSL specification.
DB Query Executor Module
Evaluates custom queries written in DSL and resolves them against indexed org metadata.
DSL Search and Executor
Executes advanced rules such as conditional logic, pattern matching, and tag group expansion.
Webhooks Module
Fetches live org data using pre-registered APIs if real-time resolution is needed. Complements indexed search with external calls.
Registry ID Convention
Each organization is associated with a registry_id that is used to register it under a broader Registry of Registries system. This enables cross-registry federation, discovery, and governance.
2. OrgObject Schema
Data Class
@dataclass
class OrgObject:
org_uri: str
org_id: str
org_spec_id: str
org_local_db_url: str
org_service_gateway_url: str
org_asset_registry_id: str
org_group_ids: List[str]
org_name: str
org_description: str
org_metadata: Dict[str, Any]
org_url_map: Dict[str, str]
org_tags: List[str]
org_spec_data: Dict[str, Any]
Field Description Table
| Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
org_uri |
str |
Computed URI in the format <org_name>:<org_spec_id> |
org_id |
str |
Unique organization identifier |
org_spec_id |
str |
Versioned spec ID for configuration |
org_local_db_url |
str |
Internal/local MongoDB or DB endpoint |
org_service_gateway_url |
str |
URL to public-facing gateway for org services |
org_asset_registry_id |
str |
Identifier for associated asset registry |
org_group_ids |
List[str] |
Array of group IDs the org belongs to |
org_name |
str |
Human-readable name |
org_description |
str |
Text description |
org_metadata |
Dict[str, Any] |
Arbitrary user-defined metadata |
org_url_map |
Dict[str, str] |
Mapping of internal service URLs |
org_tags |
List[str] |
Set of searchable tag keywords |
org_spec_data |
Dict[str, Any] |
Complete specification document for the org |
3. REST API Documentation
3.1 CRUD APIs
Create Organization
- POST
/org
curl -X POST http://localhost:5000/org \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"org_id": "org-001",
"org_spec_id": "v1",
"org_name": "ExampleOrg",
"org_tags": ["ai", "research"]
}'
Get Organization by URI
- GET
/org/<org_uri>
curl http://localhost:5000/org/ExampleOrg:v1
Update Organization by URI
- PUT
/org/<org_uri>
curl -X PUT http://localhost:5000/org/ExampleOrg:v1 \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"org_description": "Updated org description"}'
Delete Organization by URI
- DELETE
/org/<org_uri>
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:5000/org/ExampleOrg:v1
3.2 Generic Query
Query Organizations
- POST
/orgs
curl -X POST http://localhost:5000/orgs \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"org_tags": "research"}'
3.3 Specialized Queries
Get by org_id
- GET
/orgs/by-id/<org_id>
curl http://localhost:5000/orgs/by-id/org-001
Get by org_spec_id
- GET
/orgs/by-spec-id/<spec_id>
curl http://localhost:5000/orgs/by-spec-id/v1
Get by Tag
- GET
/orgs/by-tag/<tag>
curl http://localhost:5000/orgs/by-tag/research
Get by Group ID
- GET
/orgs/by-group/<group_id>
curl http://localhost:5000/orgs/by-group/group-xyz
Get by Asset Registry ID
- GET
/orgs/by-registry/<registry_id>
curl http://localhost:5000/orgs/by-registry/registry-01
Search by Name Keyword
- GET
/orgs/search-by-name?q=<keyword>
curl "http://localhost:5000/orgs/search-by-name?q=example"
Get by URL Prefix
- GET
/orgs/with-url-prefix?prefix=<prefix>
curl "http://localhost:5000/orgs/with-url-prefix?prefix=http://gateway."
Get by Metadata Key/Value
- POST
/orgs/by-metadata
curl -X POST http://localhost:5000/orgs/by-metadata \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"key": "region", "value": "asia"}'
Get Organizations with Specific Key in org_spec_data
- GET
/orgs/has-spec-key/<key>
curl http://localhost:5000/orgs/has-spec-key/runtime
4. GraphQL Endpoint
Endpoint
- POST
/graphql
Supports:
- Querying by
org_id,org_name, ortag - Nested field retrieval
- GraphiQL UI via browser
Sample GraphQL Query
query {
orgs(tag: "ai") {
org_id
org_name
org_description
org_tags
}
}
Sample cURL
curl -X POST http://localhost:5000/graphql \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"query": "query { orgs(tag: \"ai\") { org_id org_name } }"}'
Org Creation System
The Org Creation System is responsible for orchestrating the automated creation, resumption, and removal of organizations on a Kubernetes-based infrastructure. This system is modular and stage-driven, enabling granular control over each step involved in provisioning an organization.
It is designed to operate in real-time or in scheduled mode, supporting task execution via Kubernetes Jobs with full traceability of status through MongoDB and Redis.
Thank you. Here's the revised architecture documentation as per your request — with a primary focus on the Org Creator System, and a concise overview of the Init Container Flow.
Org Deployment Architecture
The Org Deployment system automates the setup of organization-specific services on Kubernetes. It is composed of two major subsystems:
- Org Creator System – a controller-layer service that accepts org specifications, validates them, and orchestrates Kubernetes container jobs to perform org creation.
- Org Creation Flow (Init Container) – a containerized job that executes the actual org initialization inside the Kubernetes cluster.
This design ensures decoupled, traceable, and policy-compliant org instantiation across federated environments.
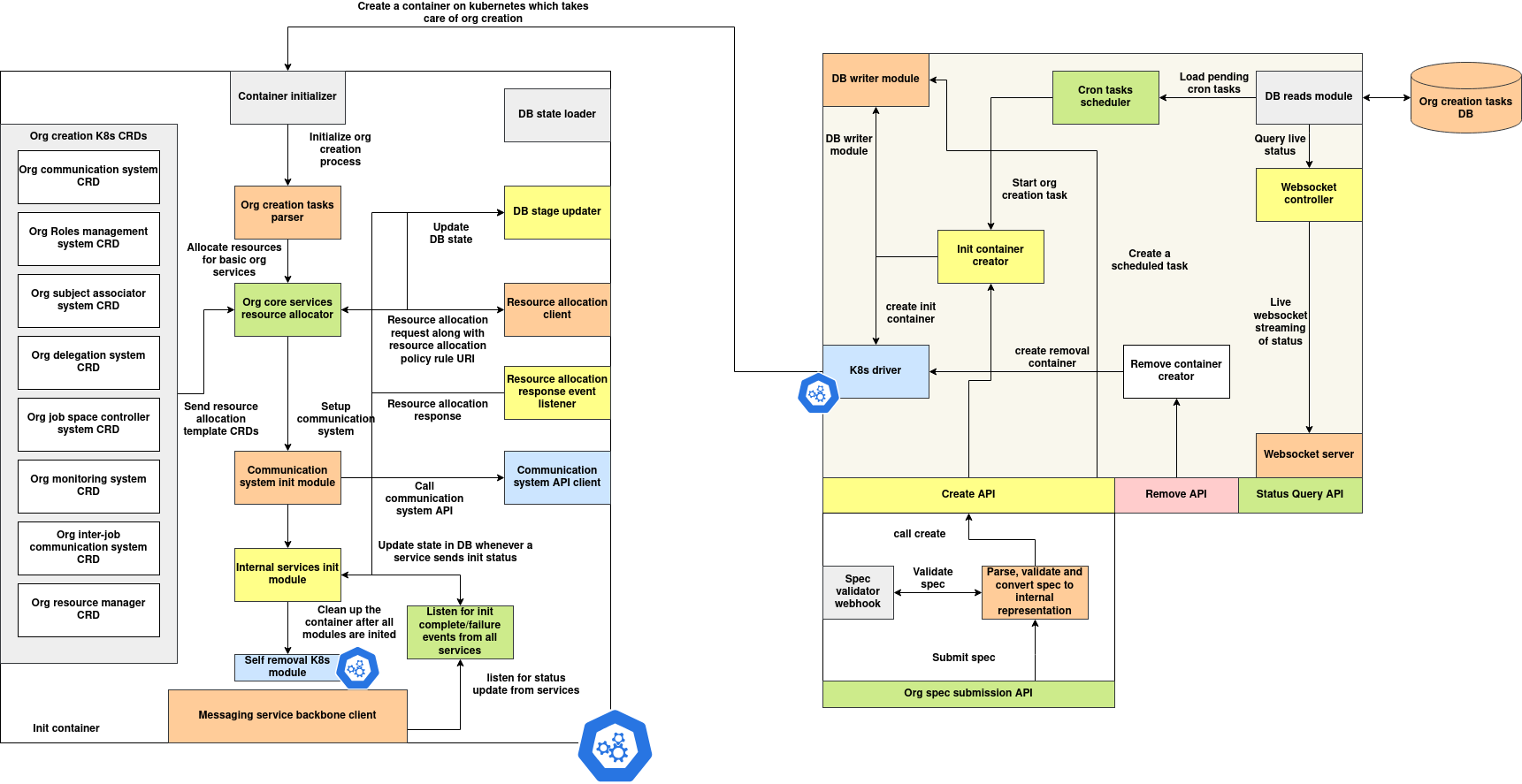
1. Org Creator System (Primary Focus)
The Org Creator System is responsible for handling org specification intake, validation, task scheduling, and initiating Kubernetes jobs that execute org creation logic inside containers.
Responsibilities:
- Receives and validates org specs
- Schedules creation as an immediate or cron task
- Uses Kubernetes APIs to create an Init Container Job
- Monitors org creation status through WebSocket and polling APIs
- Persists creation states and metadata into a centralized database
Key Components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Org Spec Submission API | Accepts incoming organization specs via REST endpoint. |
| Spec Validator Webhook | Performs structural and logical validation of submitted specs. |
| Parser and Internal Converter | Converts validated specs into actionable internal representations. |
| Create API | Triggers the creation of an init container job using the internal spec. |
| Cron Tasks Scheduler | Handles delayed or recurring org creation through scheduled tasks. |
| Init Container Creator | Constructs the Kubernetes job that runs the init container logic. |
| K8s Driver | Interacts with Kubernetes API to launch, monitor, and clean up jobs. |
| Remove Container Creator | Triggers cleanup jobs for orgs marked for removal. |
| DB Writer Module | Persists job/task lifecycle events and internal state transitions. |
| DB Reads Module | Supports status queries, cron retrievals, and live status access. |
| WebSocket Controller / Server | Streams real-time updates about org creation stages. |
| Status Query API / Remove API | Provides external clients with REST access to job status and cleanup operations. |
Process Flow:
- Spec Submission: A user submits an org spec via the
Org Spec Submission API. - Validation & Parsing: The spec is validated and converted into an internal task.
- Job Scheduling: The spec is either scheduled as a cron task or triggered immediately.
- K8s Job Creation: The
Init Container Creatorconstructs a Kubernetes Job which references the init container image and required volume/mounts/env. - Status Tracking: Job lifecycle is tracked in the DB and broadcast via WebSocket or queried via status APIs.
- Cleanup: The
Remove Container Creatorensures cleanup of resources upon task termination or manual removal.
2. Org Creation Flow (Init Container Overview)
The Init Container is a self-contained job that executes the actual orchestration steps needed to instantiate the org services.
General Flow:
- Initialization – The
Container Initializerreads and begins the org creation tasks. - Core Services Setup – The
Org Core Services Resource Allocatorprovisions essential services like monitoring, roles, communication, etc. - Resource Allocation – Template CRDs are registered and sent to Kubernetes with associated policy URIs.
- Service Bootstrapping – Each service (e.g., communication, subject associator, delegation) is initialized in order.
- Status Emission – Status updates are pushed into the messaging backbone and tracked centrally.
- Finalization – Once all modules complete, the container invokes the
Self Removal K8s Moduleto clean up itself.
Subsystems Bootstrapped:
- Org Communication System
- Org Roles and Subject Association
- Monitoring and Inter-job Communication
- Delegation and Job Control Systems
The init container is designed to be self-terminating and modular. All its operations are observed by the main Org Creator System through Kubernetes job events and DB updates.
Summary
| Aspect | Org Creator System | Org Creation Flow (Init Container) |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Environment | External service (server) | Kubernetes container job |
| Responsibilities | Spec parsing, validation, task scheduling, job creation, monitoring | Service bootstrapping, CRD application, status reporting |
| APIs Exposed | Submission API, Create API, Status Query API, Remove API | Internal-only (runs isolated) |
| Communication | Webhooks, REST, WebSocket, K8s API | Messaging backbone, K8s CRDs |
| Termination | Tracked and managed by controller | Self-destructs after successful initialization |
Core Responsibilities
-
Task Orchestration: Creates and tracks
org_creation_taskentries, each representing a full lifecycle process for an organization. -
Stage-Based Execution: Each task is broken into predefined stages such as
communication_system,roles_management_system, and others. These stages are executed in sequence or resumed individually if needed. -
Kubernetes Job Scheduling: Org creation/removal jobs are executed as Kubernetes Jobs in the
org-jobsnamespace. The system uses environment variables to pass metadata and execution parameters into the container runtime. -
Redis-Backed Scheduling (Optional): For scheduled tasks, a background
Schedulerthread checks timestamps and submits pending tasks at the right time. -
Status Management: A dedicated component (
StatusUpdateSystem) tracks and updates the completion or failure of each stage, automatically marking the overall task ascompleteorfailed.
Main Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| OrgCreationTask | Represents a full org creation process with scheduling and metadata. |
| OrgCreationStage | Individual execution units that are part of a task. |
| OrgCreationJob | Utility to create Kubernetes Jobs for new, resumed, or removal executions. |
| Scheduler | Watches for scheduled tasks and triggers them at the right time. |
| StatusUpdateSystem | Manages the state of each stage and updates the parent task accordingly. |
| Flask REST APIs | Expose endpoints to create, resume, remove, and monitor org creation processes. |
Org Creation System — Schema Documentation
OrgCreationTask Schema
This class represents the lifecycle metadata and configuration required to initiate and track an organization creation process. Each OrgCreationTask corresponds to one end-to-end creation request and contains scheduling information, execution parameters, and current status.
Data Class
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
from typing import Dict, Any
import uuid
@dataclass
class OrgCreationTask:
org_creation_task_id: str = field(default_factory=lambda: str(uuid.uuid4()))
org_spec_id: str = ''
submission_time: int = 0
status: str = ''
completion_time: int = 0
creation_schedule: str = ''
spec_data: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=dict)
Field Descriptions
| Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
org_creation_task_id |
str |
Unique identifier for the task, auto-generated as a UUID. |
org_spec_id |
str |
Identifier for the organization specification used during creation. |
submission_time |
int |
UNIX timestamp indicating when the task was submitted. |
status |
str |
Current status of the task. Values: pending, processing, complete, failed. |
completion_time |
int |
UNIX timestamp indicating when the task finished (success or failure). |
creation_schedule |
str |
Scheduled execution time in UNIX timestamp string format. Use -1 for immediate execution. |
spec_data |
Dict[str, Any] |
Arbitrary dictionary holding deployment metadata such as kubeconfig and configuration overrides. |
OrgCreationStage Schema
Each OrgCreationStage represents a unit of execution within an org creation task. A task is composed of multiple stages that are executed sequentially or resumed individually.
Data Class
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
import uuid
@dataclass
class OrgCreationStage:
stage_id: str = field(default_factory=lambda: str(uuid.uuid4()))
org_creation_task_id: str = ''
stage_type: str = ''
status: str = ''
completion_time: str = ''
Field Descriptions
| Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
stage_id |
str |
Unique identifier for the stage, auto-generated as a UUID. |
org_creation_task_id |
str |
Foreign key referencing the parent org creation task. |
stage_type |
str |
Logical name of the stage (e.g., communication_system, roles_management_system). |
status |
str |
Current status of the stage. Values: pending, complete, failed. |
completion_time |
str |
ISO-8601 formatted timestamp string indicating when the stage completed. |
Org Creation Stages — Functional Breakdown
Each organization creation task consists of a predefined sequence of stages, executed in order. Each stage is responsible for provisioning a specific subsystem or capability within the organization. These stages are independently tracked and can be resumed individually in case of failure.
Below is a detailed explanation of each stage.
| Stage Type | Description |
|---|---|
communication_system |
Sets up the messaging or event-driven infrastructure for the organization. This typically includes internal queues, pub/sub channels, and protocol gateways required for inter-component communication. |
roles_management_system |
Provisions and registers role definitions, access groups, and permission hierarchies for subjects (users, agents) within the organization. |
subject_association_system |
Binds users, devices, or agents to specific roles or entities. This may include identity mapping, group membership, and initial subject metadata. |
delegation_system |
Initializes delegation logic such as task assignment rules, hierarchical control flows, or policy-based authority chains between subjects. |
job_space_controller |
Deploys execution environments or job orchestration mechanisms (e.g., task queues, containers, DAG runners) for managing compute workloads associated with the organization. |
resource_manager |
Provisions required storage volumes, memory and compute resources, and quota control mechanisms. Ensures infrastructure-level support for the organization's activities. |
monitoring_system |
Installs and configures metrics collection, log aggregation, and health monitoring services to track performance, detect failures, and audit system behavior. |
Each of these stages is implemented as part of a Kubernetes Job and controlled via environment variables passed at runtime. These stages are idempotent and can be resumed if a previous execution fails. The completion or failure of each stage determines the outcome of the overall org creation task.
Org Creation System — API Reference (CRUD for Tasks and Stages)
This section documents the REST APIs for managing OrgCreationTask and OrgCreationStage entities. These endpoints support create, read, update, delete, and query operations.
All APIs assume JSON request and response format.
1. Org Task APIs
POST /org-task
Create a new org creation task.
curl -X POST http://<host>/org-task \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"org_spec_id": "spec123",
"submission_time": 1716900000,
"status": "pending",
"completion_time": 0,
"creation_schedule": "-1",
"spec_data": {
"kubeconfig": { ... }
}
}'
Response:
201 Created: Task inserted successfully.400 Bad Request: Validation or database error.
GET /org-task/<task_id>
Fetch a task by its ID.
curl -X GET http://<host>/org-task/123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000
Response:
200 OKwith task data.404 Not Foundif task does not exist.
PUT /org-task/<task_id>
Update a task partially.
curl -X PUT http://<host>/org-task/<task_id> \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"status": "processing"}'
Response:
200 OKon success.404 Not Found: Task not found.400 Bad Request: Update failed.
DELETE /org-task/<task_id>
Delete a task from the database.
curl -X DELETE http://<host>/org-task/<task_id>
Response:
200 OKif deleted.404 Not Foundif task was missing.
POST /org-tasks
Query tasks using arbitrary filters.
curl -X POST http://<host>/org-tasks \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"status": "pending"}'
Response:
200 OKwith matching list.400 Bad Request: Query error.
2. Org Stage APIs
POST /org-stage
Create a new stage for a task.
curl -X POST http://<host>/org-stage \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"org_creation_task_id": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
"stage_type": "monitoring_system",
"status": "pending",
"completion_time": ""
}'
Response:
201 Createdon success.400 Bad Requeston failure.
GET /org-stage/<stage_id>
Fetch a stage by its ID.
curl -X GET http://<host>/org-stage/<stage_id>
Response:
200 OKwith stage data.404 Not Found: If stage is missing.
PUT /org-stage/<stage_id>
Update status or metadata of a stage.
curl -X PUT http://<host>/org-stage/<stage_id> \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"status": "complete", "completion_time": "2025-05-28T16:00:00Z"}'
Response:
200 OKif updated.404 Not Foundor400 Bad Requestotherwise.
DELETE /org-stage/<stage_id>
Delete a stage from DB.
curl -X DELETE http://<host>/org-stage/<stage_id>
Response:
200 OKon successful deletion.404 Not Foundif stage is missing.
POST /org-stages
Query stages by task ID or other filters.
curl -X POST http://<host>/org-stages \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"org_creation_task_id": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000", "status": "pending"}'
Response:
200 OKwith matching stages.400 Bad Requeston error.
Org Creation System — Execution APIs
This section documents the operational APIs responsible for executing, resuming, removing, and updating the status of org creation tasks. These endpoints interact with the task and stage databases and trigger Kubernetes Jobs.
All APIs are prefixed with /org-creation/.
API: Submit Org Creation Task
POST /org-creation/submit/<org_creation_task_id>
Submits a pending org creation task for execution. This triggers the creation of all defined stages and starts a Kubernetes Job.
curl -X POST http://<host>/org-creation/submit/abcd1234
Response:
200 OKif submitted successfully.500 Internal Server Errorif the task is invalid or job creation fails.
API: Resume Org Creation from a Stage
POST /org-creation/resume/<stage_id>
Resumes an org creation process from a given failed or incomplete stage.
curl -X POST http://<host>/org-creation/resume/xyz987
Response:
200 OKif resumed successfully.500 Internal Server Errorif resume fails.
API: Remove Org
POST /org-creation/remove/<org_creation_task_id>
Initiates cleanup and deletion of an already provisioned org by launching a Kubernetes job with MODE=remove.
curl -X POST http://<host>/org-creation/remove/abcd1234
Response:
200 OKif removal job started.500 Internal Server Erroron failure.
API: Update Stage Status
POST /org-creation/status-update/<stage_id>
Updates the status of a single stage. Automatically updates the parent task if all stages are complete or if a stage fails.
curl -X POST http://<host>/org-creation/status-update/xyz987 \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"status": "complete",
"completion_time": "2025-05-28T15:30:00Z"
}'
Response:
200 OKif the stage was updated and any dependent logic was executed.400 Bad Requestor500 Internal Server Erroron failure.
Execution Flow
This section outlines the internal steps performed when each API is invoked.
1. Submitting an Org Creation Task
- The system fetches the task from the database using
org_creation_task_id. - Predefined stages (e.g.,
communication_system,resource_manager, etc.) are created withstatus="pending". -
A Kubernetes job is launched in the
org-jobsnamespace with: -
Task ID
- Stage IDs
- Registry API URL
- The task’s status is updated to
"processing".
2. Resuming from a Stage
- The system fetches the stage and corresponding task from the database.
- All stage IDs for the task are collected.
-
A Kubernetes job is launched with:
-
Task ID
- All stage IDs
RESUME_STAGE_IDset to the failed stage- The resumed job begins execution from the specified stage.
3. Removing an Organization
- The task is retrieved to access its kubeconfig and metadata.
-
A Kubernetes job is launched with:
-
Task ID
MODE=removepassed as environment variable- No stages are executed; instead, a teardown routine is run inside the job.
4. Updating a Stage Status
- The specified stage is updated in the database with the new status.
- If the stage is marked
failed, the parent task is immediately updated tofailed. -
If the stage is marked
complete, the system checks all sibling stages: -
If all are
complete, the parent task is updated tocomplete.